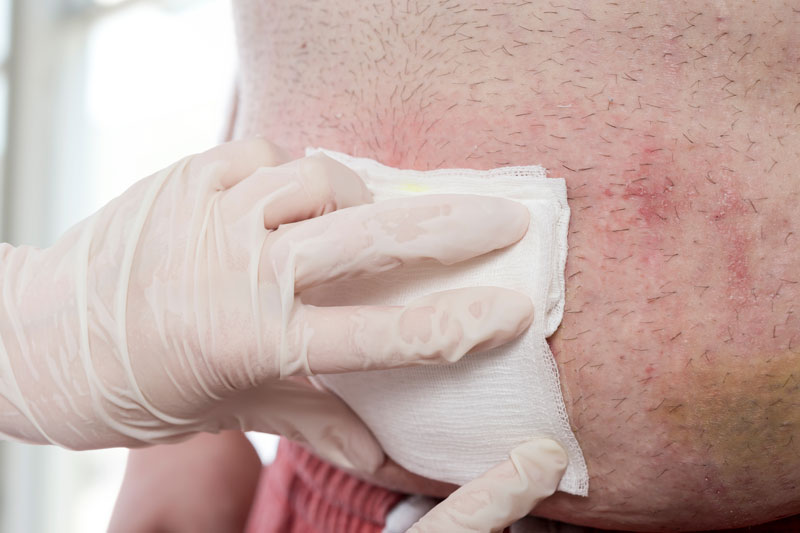
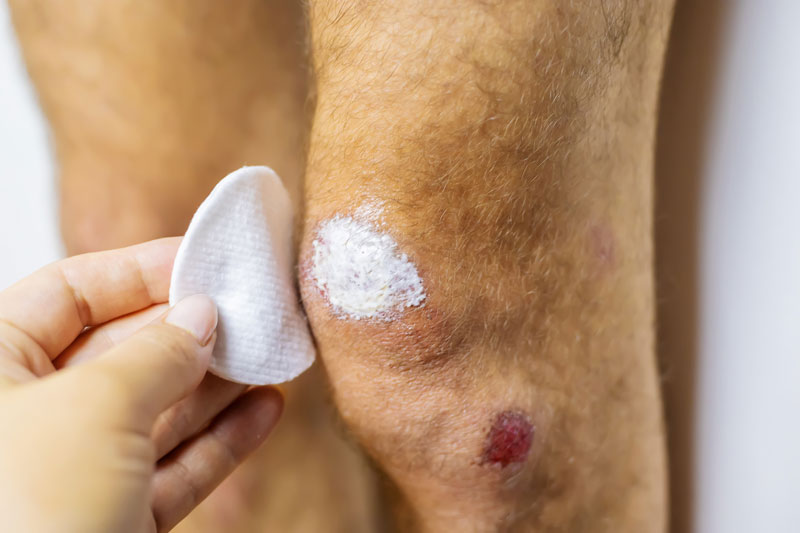
What are Surgical Wounds?
What Causes Surgical Wounds?
Symptoms of Surgical Wounds
Symptoms of surgical wounds can vary depending on the type of surgery and the healing process. Common symptoms may include:
- Pain or Discomfort: Mild to moderate pain or discomfort around the surgical site is typical and can be managed with prescribed pain medications.
- Swelling: Some swelling around the incision site is normal and usually subsides as the wound heals.
- Redness and Warmth: Mild redness and warmth at the wound site are common responses to the body’s healing process.
- Drainage: Minimal drainage of clear or slightly yellow fluid may occur from the incision during the initial healing stages.
- Slight Bleeding: Minor bleeding or oozing might be present initially but should diminish over time.
- Incision Appearance: The incision site may appear slightly raised, firm, or pink during the healing process.
- Fever: In some cases, a low-grade fever may develop as a natural response to surgery.
- Advanced Wound Healing Modalities: Employing growth factors, cellular therapies, or skin substitutes to enhance healing in complex cases.
It’s essential to monitor the surgical wound closely and promptly report any concerning symptoms, such as excessive bleeding, increasing redness, pus-like drainage, or high fever, to the healthcare provider for further evaluation and appropriate management. Proper care and attention during the post-operative period are vital to ensure successful wound healing and a smooth recovery.
Treatment Options for Surgical Wounds
Proper treatment for surgical wounds is crucial to promote optimal healing and prevent complications. The following are some common treatment options for surgical wounds:
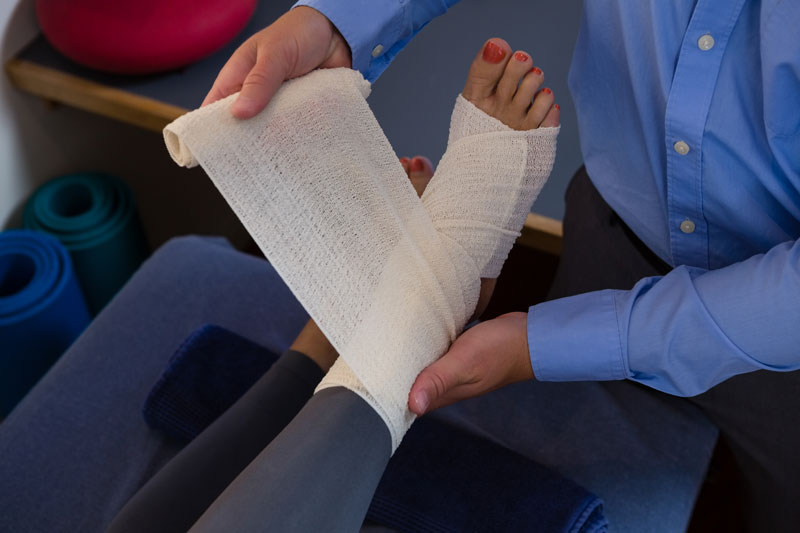
- Wound Dressings: Applying appropriate wound dressings to protect the incision site, promote a moist wound-healing environment, and minimize infection risk.
- Sutures or Staples Removal: Ensuring timely removal of sutures or staples based on the surgeon’s instructions to facilitate proper wound closure.
- Wound Cleaning and Care: Cleaning the wound as directed and following specific wound care instructions provided by healthcare professionals.
- Pain Management: Utilizing pain medications and other pain relief techniques to manage post-operative discomfort.
- Infection Prevention: Administering antibiotics or other antimicrobial treatments to prevent or treat infection, if necessary.
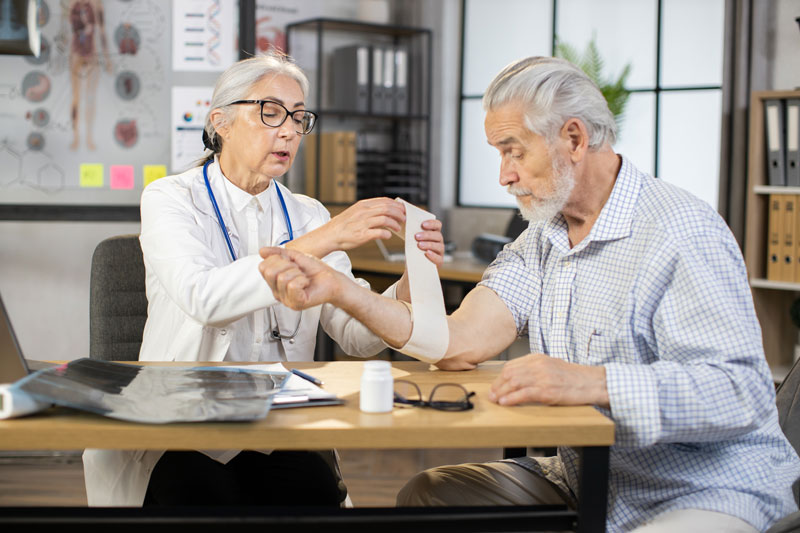
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regularly monitoring the wound’s healing progress and scheduling follow-up appointments to ensure proper recovery and address any concerns promptly.
Frequently Asked Questions about Surgical Wounds
1. How long does it take for a surgical wound to heal?
The healing time for a surgical wound can vary depending on several factors, including the type of surgery, the size and location of the incision, the individual’s overall health, and how well they follow post-operative care instructions. In general, most surgical wounds heal within two to three weeks, with the incision site gradually closing and forming a scar. However, complete healing and scar maturation may take several months. It’s essential to follow the healthcare provider’s guidance, maintain good wound care practices, and attend scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.
2. What should I do if my surgical wound is not healing properly?
If you notice that your surgical wound is not healing as expected, or if you experience any concerning symptoms such as increased pain, redness, swelling, drainage, or signs of infection, it is crucial to contact your healthcare provider promptly. They can evaluate the wound, identify potential issues, and provide appropriate treatment or interventions. Delayed wound healing can be caused by various factors, such as infection, poor blood flow, or underlying health conditions. Seeking timely medical attention ensures that any complications are addressed promptly, promoting better wound healing and a smoother recovery process.